|
This post is completed by 1 user
|
Add to List |
106. Reverse a Doubly-Linked List (In-place Algorithm)
Objective: Given a doubly-linked list, write an in-place algorithm to reverse the list.
Example:
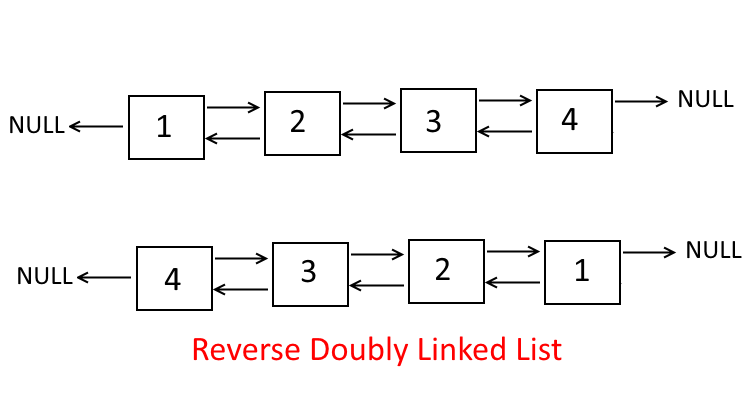
Approach:
- Every Node in a doubly-linked list has the next and previous pointer.
- Do the linear traversal of the linked list and keep swapping the next and previous pointers.
- In the end, make the last pointer the head of the list.
Output:
->4->3->2->1 ->1->2->3->4

